MacBook screen issue troubleshooting focuses on identifying hardware-related display defects such as lines, color spots, abnormal tint, and pressure damage. These problems are typically caused by LCD panel degradation, backlight failure, or physical stress rather than software issues. Correct diagnosis and reliable screen replacement are essential to restore normal display performance and prevent repeat failures.
MacBook screen issue troubleshooting basics
During MacBook screen issue troubleshooting, most visible defects originate from the LCD panel or backlight assembly. If the issue appears during startup, remains unchanged across different brightness levels, and does not affect an external monitor, the screen itself is the source of the problem.
Display defects can be grouped into three main categories: line-related issues, color and spot abnormalities, and pressure damage.
Lines and shadow-related display issues
Problems such as black lines across MacBook Pro screen, black lines at bottom of MacBook Pro screen, and MacBook Pro shadows bottom screen are caused by failures within the LCD matrix or its driver circuits.
Technically accurate causes include:
-
Partial failure of LCD row or column drivers
-
Degradation of panel bonding between glass and driver IC
-
Internal signal interruption within the LCD layer
-
Aging of the panel after long-term use
These issues are not affected by macOS settings or GPU performance. Once lines or shadows are visible, the damage is permanent and screen replacement is required.
Color spots and abnormal screen tint
Color-related problems such as orange spot on MacBook screen, orange smudge on MacBook Pro screen, MacBook Pro orange screen, and MacBook screen white tint are usually caused by changes in the optical layers of the display.
Correct underlying reasons include:
-
Uneven aging of the backlight LED array
-
Deterioration of light diffusion and color filter layers
-
Localized thermal stress over time
These defects remain visible on light backgrounds and do not move or disappear. They indicate irreversible changes inside the panel and cannot be corrected through calibration or software adjustments.
Pressure damage on MacBook screens
MacBook screen pressure damage and pressure damage MacBook Pro screen issues occur when external force deforms the LCD layers.
Common real-world causes:
-
Closing the lid with foreign objects on the keyboard
-
Uneven pressure during transportation
-
Improper handling during disassembly or installation
Pressure damage usually appears as fixed dark or discolored areas. The shape remains consistent regardless of brightness or content, confirming physical deformation of the panel.
Repair decision and replacement considerations
A correct troubleshooting process includes:
-
External monitor testing to confirm GPU function
-
Observation during boot to rule out software influence
-
Visual inspection for fixed patterns or color changes
If defects are isolated to the internal display, replacement of the complete screen assembly is the only stable repair solution. Partial repairs or software resets do not resolve panel-level failures.
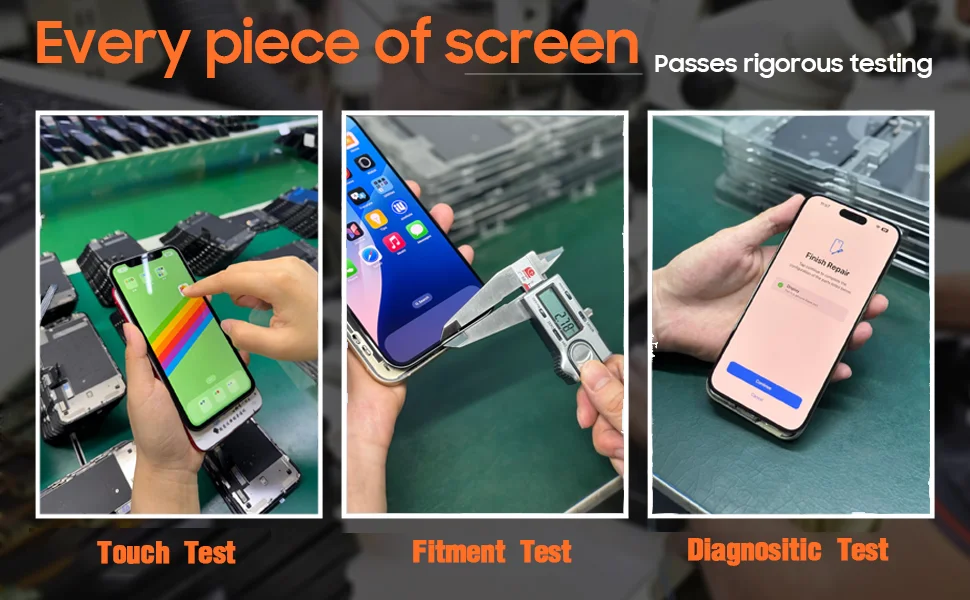
Quality control process for MacBook replacement screens
To reduce common display defects and ensure stable performance after installation, Wellworth applies a structured quality control process to every MacBook replacement screen.
Display appearance inspection
Each screen is visually inspected to ensure:
-
No scratches or surface damage
-
No stains, marks, or cosmetic defects
-
Clean edges and intact flex cables
Display performance testing
Screens are powered on to confirm:
-
No black lines or spots
-
Correct color performance without orange or white tint
-
No screen bleeding at the edges
-
No flickering at different brightness levels
Functional testing on motherboard
Each screen is tested on a compatible motherboard to verify:
-
Automatic brightness adjustment works correctly
-
Ambient light sensing functions normally
-
Camera operation is stable and properly recognized
This QC process helps prevent issues such as black lines, color abnormalities, flickering, and functional incompatibility before screens are supplied for repair use.
Conclusion
MacBook screen issue troubleshooting relies on identifying permanent panel defects caused by aging, material degradation, or physical stress. Lines, color spots, abnormal tint, and pressure damage are hardware failures that require screen replacement rather than software repair.
For repair businesses and wholesalers seeking consistent repair outcomes, using replacement screens that have passed strict appearance inspection, display testing, and motherboard verification, helps reduce returns, repeat repairs, and post-installation issues.